Tel/WhatsApp
Tel/WhatsApp
Wheat starch and gluten manufacturing
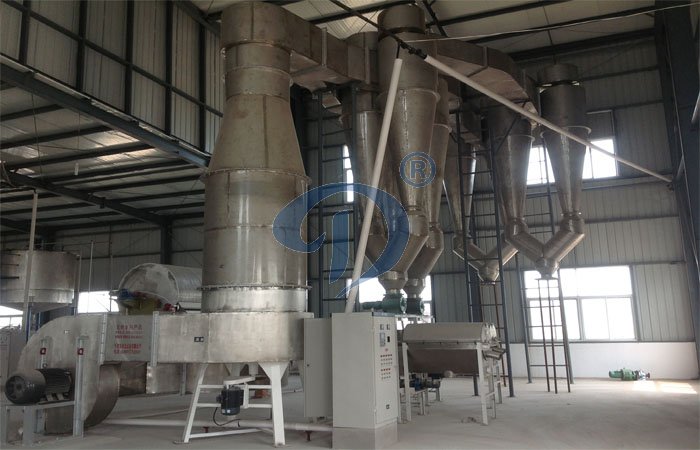

Drying machine wheat starch
Wheat Starch and gluten manufacturing is a wet process . One kind wheat starch and gluten manufacturing process called Martin process.
Martin process of wheat starch and gluten manufacturing involves mixing flour and water to make a developed dough . The dough is then washed in a variety of mixing troughs with large amounts of water to get purified gluten and diluted starch milk , which is then concentrated and separated into A and B starch .
Another principal difficulty with wheat starch and gluten manufacturing lies in separating the two because each has very different physical properties. Gluten is awkward to extract from a parent flour because of its rubbery stickiness.
A major factor in any decision to build a wheat starch and gluten manufacturing factory is the market for its products. Such a factory manufactures five main products: "A" (or primary) starch, gluten, "B" (or secondary) starch, solubles and bran . The market must be able to support competitively the profitable disappearance of these goods.
The uses of "A" starch are found foremost in the fine paper and food industries, where low protein maize starch and farina (potato starch) compete. Modified starches can also be derived for either industry. In the fine paper industry, "A" starch is used for sizing. "A" starch also is incorporated in many varieties of food and is used as a feedstock for ethanol production and conversion into glucose syrups. In some countries, "A" starch is sold in wet or slurry form and transported in tankers. This cuts out the need for drying to a powder. Gluten today is sold as a powder, although in the past it was common to trade it in wet form in some countries. "B" starch is marketed in the adhesive and corrugated paper industries, as well as for food. Solubles are marketed in syrup form for ruminants.

Wheat starch and gluten making machine
The input for a wheat starch and gluten manufacturing factory is wheat flour. The nature of the particular wheat flour will vary from location to location depending on wheat variety, quality, price and availability.
Typical yields from a wheat starch process will be between 50% and 54% of "A" starch at less than 0.4% protein, 8% to 12% of gluten at 75% protein, 6% to 10% of "B" starch at less than 1.2% protein and 14% to 20% solubles at up to 4% protein, all expressed on a dry basis. But yields can vary considerably from these examples.
Remember that wheat starch extraction is some five times greater than gluten in wheat starch and gluten manufacturing factory — even though the revenues are roughly equal — and the personnel skills needed are very different from flour milling in certain respects.
All in all, wheat starch and gluten manufacturing is an exciting and fascinating business.Weclome to contact us if you are interested in wheat starch and gluten manufacturing.
-
 Why are the costs of transporting goods in Africa so high?
Why are the costs of transporting goods in Africa so high?
-
 Why invest in the cassava processing business in Nigeria?
Why invest in the cassava processing business in Nigeria?
-
 Financial analysis of cassava flour production in Cameroon
Financial analysis of cassava flour production in Cameroon
-
 Is cassava flour plant a profitable business in Uganda?
Is cassava flour plant a profitable business in Uganda?
-
 How long will it take to ship cassava processing machine to Nigeria?
How long will it take to ship cassava processing machine to Nigeria?